Photo: Mirimus Labs image
The Belmont School Committee took the first steps in implementing a testing regime that could spur students to return full-time to the classroom.
Promoted by School Committee Chair Andrea Prestwich and a group of parents acting as ad hoc advisors, testing would provide students and teachers the necessary “peace of mind” as they prepare to reenter schools.
“One thing that will add considerably to the safety of in-person learning is surveillance testing,” said Prestwich, as the committee unanimously supported a proposal for the school administration to look at the feasibility and logistics of surveillance testing at Belmont Public Schools.
The School Committee will update the testing proposals at its Tuesday meeting, Sept. 29.
Kate Jeffrey, a Harvard-affiliated academic scientist and the parent of a Burbank first grader, presented a plan created by fellow parents, Jamal Saeh and Larry Schmidt, that recommends the district continue its safety and health protocol such as proper social distancing and wearing masks with weekly surveillance tests and contract tracing through the town’s Health Department.
Both Jeffrey and Prestwich said the lack of guidance by the state and the federal government on the use and type of surveillance testing has forced Belmont’s hand on moving on its own to establish its own standards.
Unlike diagnostic tests that are performed on individuals who have symptoms, surveillance testing seeks out the infection within a population which in Belmont’s case will be the school district.
While the CDC does not promote its use, “surveillance testing is the only way to bring [the school district] back to normalcy,” said Jeffrey.
Not that Belmont is that far from putting students back into the classrooms. With biweekly community data showing a less than one percent infection rate per 100,000 residents and school-age rates less than a half of one percent, Jeffrey said the anticipated current number of positive COVID-19 cases of the 5,000 students in the district would be three.
And while it would be optimum that there would be no risk, Jeffrey said that is simply unrealistic so the best can be done is to reduce the overall risk with surveillance testing to increase the amount of time students can stay in class.
While most people will associate COVID-19 testing with a swab rammed into the nasal cavity, methods have advanced where saliva – drawn into a straw than placed into a container – is used to extract the RNA that are highly specific pinpointing the virus. While there are false positives at about 3 percent – Jeffrey noted half of peanut allergy tests produce false positive results – they can be detected when the individual goes to their physician.
The recommended affective options available would be fast test produced by Mirimus Labs which will analyze a pool of 25 saliva samples, about the size of a classroom, with the ability to identifying a positive case within 12 hours. The Brooklyn-based firm can breakdown the large sample into pairs and determine which students will need to seek treatment.
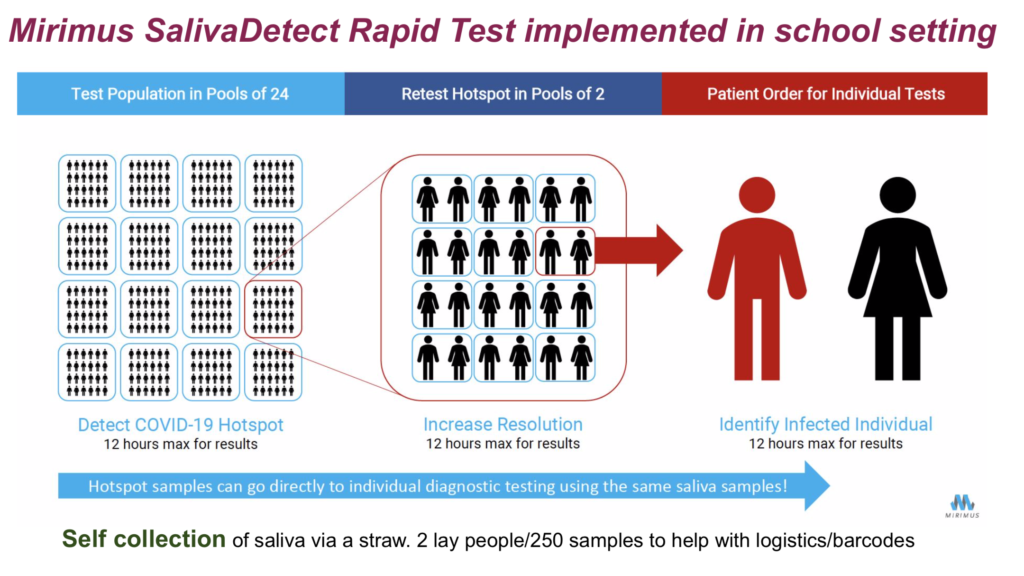
Jeffrey said Mirimus can begin sample testing within two days after being selected. It would need two volunteers to collect the saliva and fill out the data forms for every grouping of 250 students.
After the first week in which all students and teachers would take the test to establish a baseline number, each subsequent week 10 percent of students – approximately 500 students – and all educators would be tested. The baseline test will cost $80,000 and the subsequent cost for the school year will be approximately $500,000.
Fundraising, possible federal or state expenditures and future lower cost testing could fund the proposal.
Jeffrey’s recommends the district start with the available Mirimus lab-based technology, than switching to a cheaper point-of-care approach when one becomes available likely by the end of the year.

While this new testing remains important for the community by supplying information on COVID, its greatest benefit “really has to be in returning students to the classroom,” said Jeffrey.
A second testing scheme – reviewed by Prestwich and Dr. Kate Rodriguez-Clark – is to sample the wastewater at the six school buildings. COVID is present in fecal matter so testing would involve the weekly collection of sewage from each school. The samples would be tested by a company like Biobot Analytics that can identify a single infection from the samples. The cost would be $8,500 a week for all buildings.
The advantage of using wastewater testing is it works well in tandem with the saliva testing in tracking the virus and it is easier to collect a sample. One negative is a person with the coronavirus must use the restroom at the school for the sample to register a positive case. Describing the dilemma resulted in Prestwich likely uttering the first mention of the slang definition of solid waste from the body in a future school committee minutes.
“The bottom line is that if the person who was infected with COVID doesn’t poop at school then we will not detect it … and that’s a drawback,” said Prestwich.
While calling the overall testing proposal “an exciting opportunity” to increase the peace of mind of educators and the public, Belmont Superintendent John Phelan said it will be a challenge to see how the district “operationalize” testing with the knowledge that the district has 4,500 student and 625 staff member between the ages of 3 and well past 60.
School Committee member Kate Bowen wondered aloud how necessary a costly surveillance testing regiment is for Belmont after the school district had “taken great steps in improving the buildings” including increasing the air flow in all school rooms and as the community has a very low rate of infection.
Prestwich noted that while the town’s “rates are low at this point … COVID increases exponentially if you don’t keep a lid on it.”
“Hopefully the precautions that we can take will prevent the numbers from shooting up,” she said.